|
| SESSION 3 Part3 |
|
Java's execute form |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
One of Java's characteristics is
"Write Once, Run Anywhere"
(Once written, it can be run anywhere).
Once you made soft with Java,
you don't have to create soft for each OS.
You see, normally games are separated like,
games for Mac or Windows.
If a soft is made with Java,
the same one can be run anywhere. |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
I see, that means
you only need
one CD-ROM. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
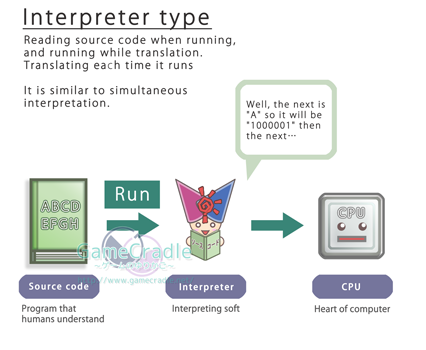
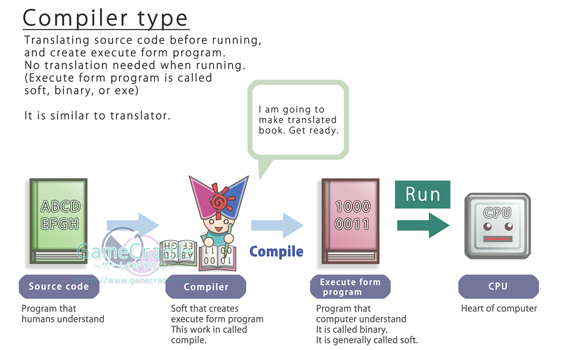
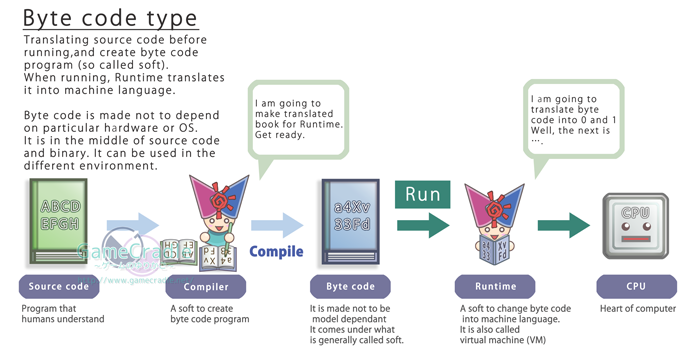
That is because
Java is operating with
structure which is called
Byte code.
We have already looked at
execute form, remember?
Like Compile type or
Interpreter type.
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
Hey,
you do remember a little bit,
don't you?
It is about how to run
program.
Remember how
you drew the picture of a
morooon kid….
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
It is not
morooon!
It is called "Poncho"!
Oh, that one.
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
……
Java's execute form is
called byte code that adopted
both systems of interpreter and compiler.
Hopefully, you would remember as you read. |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
I do remember.
I am serious.
Hey,
you told me to
just have a quick look. |
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
Characteristic of execute form |
| |
| |
Interpreter type |
Byte code type |
Compiler type |
|
What is needed to run |
Source code
and
Interpreter soft |
Byte code
and
Runtime soft |
Execute form program
(binary form)
Usually called as Soft |
| Number of translation |
|
Every time |
|
Because interpreter translates as it runs. |
|
|
Every time |
|
Because interpreter translates as it runs. |
|
|
Once |
| Not needed after execute form program is
created. |
|
| Speed |
| Slow |
| Because interpreter translates as it runs. |
|
| A bit fast |
|
Because intermediate code translates as it runs |
|
| Fast |
|
Because it only keeps running machine language
that has been already translated. |
|
| Machine-dependence |
| Low |
When it is run by different kind of CPU or OS,
as long as there is "interpreter" for the model,
it can be run by any computer.
|
|
| Low |
When it is run by different kind of CPU or OS,
as long as there is "interpreter" for the model,
it can be run by any computer.
|
|
| High |
When it is run by different kind of CPU or OS,
execute form program needs to be recreated
because machine language is different.
|
|
| Confidentiality |
| Low |
Distribution of source code is compulsory to
run. Therefore, when it is read, it is easy to
understand the content.
|
|
| A bit high |
|
Because byte code is turned into byte data, it
can not be read as it is. |
|
| High |
Distribution of source code is not necessary to
run. Because execute form is "0" and "1", it can
not be read as it is.
|
|
| Remark |
Language called Script often uses this form. |
This form adopts the advantages of interpreter and
compiler
Byte code=Soft |
Desktop soft such as game often uses this form.
So called "the form for creating soft". |
|
※Current Java adopts high speed technology such
as JIT compile style (Changing byte code into
machine language at the first run, and not
translating afterwards), therefore it does not
always match with the characteristics of this
table
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
OK, OK |
 |
【Double Click】
To push a
button of mouse
twice in a row… |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
Byte code is
what is generally called "Soft".
It can be set to start with
double click, so
it feels just like
normal soft. |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|